NixOS on ARM/PINE A64-LTS
| PINE A64-LTS | |
|---|---|

| |
| Manufacturer | PINE64 (Pine Microsystems Inc.) |
| Architecture | AArch64 |
| Bootloader | Upstream U-Boot[1] |
| Boot order | SD, eMMC, SPI NOR Flash |
| Maintainer | samueldr |
The PINE A64-LTS is an affordable "Long Time Supply" single board computer built around the Allwinner R18 SOC.
It can boot from SD or from an eMMC.
Status
Upstream NixOS AArch64 image boots on the PINE A64-LTS, using the proper upstream U-Boot.
U-boot support has been added 2018-03-18. The bootloader with SPL can be downloaded from this location:
Installation instructions
To use the generic installation image for your board, you will need to copy it verbatim to an SD card.
sudo dd if=sd-image-aarch64-linux.img of=/dev/DEVICE conv=sync status=progress
This board requires the installation of u-boot at a specific location on the storage where NixOS was written to.
sudo dd if=u-boot-sunxi-with-spl.bin of=/dev/DEVICE bs=1024 seek=8
Flashing U-Boot to the SD card can be skipped if it is installed to the SPI NOR flash
These instructions can also be followed for installation on the eMMC module. A compatible eMMC writer may be required to flash the eMMC. If you do not have one available, it is possible to boot another operating system on the A64-LTS and from there dd to the eMMC.
Then, continue installation using the installation and configuration steps.
Serial console
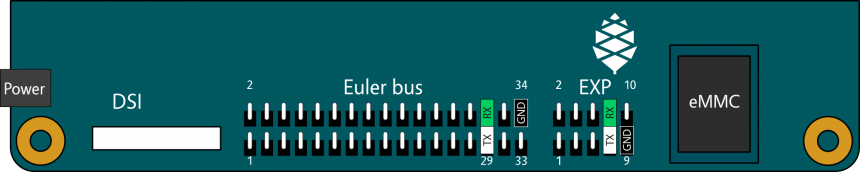
Follows a simplified drawing of the edge of the Pine A64-LTS, with two locations to tap for serial.[2][3]
| EXP Connector | |
|---|---|
| Pin | Function |
| 7 | UART0_TX |
| 8 | UART0_RX |
| 9 | GND |
| Euler "e" Connector | |
| Pin | Function |
| 29 | UART0_TX |
| 30 | UART0_RX |
| 33 | GND |
Compatibility notes
| Mainline kernel | |
|---|---|
| Ethernet |
|
| HDMI |
|
Downstream kernel
Using a kernel based on the downstream patches, it is possible to get both Ethernet and HDMI working.
Follows an example derivation and overlay to build the known working fork.
# linux-pine64.nix
{ fetchFromGitHub, buildLinux, ... } @ args:
buildLinux (args // rec {
version = "4.14.23";
modDirVersion = "4.14.23";
extraMeta.branch = "4.14";
src = fetchFromGitHub {
owner = "CallMeFoxie";
repo = "linux";
rev = "f0899693d21e15ce32df4d4702f236dfe3e0eba7";
sha256 = "043q7v7c5w84dnbgsmz117q712ljqrgay5707pz4vnvxl53czk4h";
};
extraMeta.platforms = [ "aarch64-linux" ];
structuredExtraConfig = {
# Options for HDMI.
# Fixes this:
# sun4i-drm display-engine: master bind failed: -517
SUN8I_DE2_CCU = "y";
};
} // (args.argsOverride or {}))
# overlay.nix
self: super:
let
inherit (super) callPackage kernelPatches;
in
{
linux_pine64_4_14 = callPackage ./linux-pine64.nix {
kernelPatches = [
kernelPatches.bridge_stp_helper
kernelPatches.modinst_arg_list_too_long
];
};
linuxPackages_pine64_4_14 = self.linuxPackagesFor self.linux_pine64_4_14;
}
Clusterboard Ethernet
It appears that Ethernet with the pine64 clusterboard requires a slightly modified device tree to work. There's some conflicting information about exactly what is needed to get Ethernet working but currently, mainline linux (5.4.58 at the time of testing) plus a modified device tree is sufficient to get a full speed 1gbps connection.
First create the device tree overlay.
/* sopine-baseboard-ethernet.dts */
/dts-v1/;
/ {
model = "SoPine with baseboard";
compatible = "pine64,sopine-baseboard\0pine64,sopine\0allwinner,sun50i-a64";
fragment@0 {
target-path = "/soc/ethernet@1c30000";
__overlay__ {
allwinner,tx-delay-ps = <500>;
};
};
};
Create the device tree binary from that.
dtc -O dtb -o sopine-baseboard-ethernet.dtbo -b 0 sopine-baseboard-ethernet.dts
And add it to your configuration.nix
...
hardware.deviceTree.enable = true;
hardware.deviceTree.overlays = [
"${/path/to/sopine-baseboard-ethernet.dtbo}"
];
...
SPI NOR flash
The Pine A64-LTS is equipe with a 4MB SPI NOR flash chip. The CPU will read the bootloader from it, after trying the SD card and the eMMC.
Flashing U-Boot to the SPI NOR flash will allow booting the sd-image-aarch64.img based images without further manipulating the image or the boot device (e.g. without embedding U-Boot to the usb drive). It may also allow booting UEFI compliant AArch64 images, though this is unverified.
The author did not find ways to flash the NOR flash from a running Linux system using the mainline kernel.
Flashing from FEL
The easiest method to trigger FEL mode is to not have previously flashed the SPI NOR flash with a valid bootloader, and to remove all storage devices used to boot. The Pine A64-LTS will fallback to FEL mode.
To connect the Pine A64-LTS to the computer in FEL mode, you will need a USB A-to-A (male to male) cable, and plug to the upper USB port[4].
Once started in FEL mode, the computer should see the following device.
Bus ___ Device ___: ID 1f3a:efe8 Onda (unverified) V972 tablet in flashing mode
It is, then, possible to use sunxi-fel from sunxi-tools to flash the a bootloader to the SPI NOR flash.
$ nix-shell -p sunxi-tools [nix-shell:~]$ sudo sunxi-fel -l USB device ___:___ Allwinner A64 ________:________:________:________ [nix-shell:~]$ sudo sunxi-fel -p spiflash-write 0 u-boot-sunxi-with-spl.bin 100% [================================================] 575 kB, 96.9 kB/s
Once complete, unplug the power from the Pine A64-LTS, unplug the Pine A64-LTS from the host computer, and try booting without storage devices, but either serial or HDMI. When successful, U-Boot will start, and eventually try to network boot.
Flashing from U-Boot
It is possible, through using a U-Boot bootloader built from the u-boot-sunxi tree, to write to the SPI NOR flash. The ayufan-pine64/bootloader-build has such a build. Using the released .img files, it is possible to write their custom build or erase their custom build. From their custom build, it is possible to write to the SPI NOR flash using the sf command[5].
# Detect the SPI NOR flash
=> sf probe
SF: Detected w25q128bv with page size 256 Bytes, erase size 4 KiB, total 16 MiB
# Sanity checks
=> ls mmc 0:1
558296 u-boot.bin
1 file(s), 0 dir(s)
# Loading the bootloader from an SD card
=> load mmc 0:1 ${kernel_addr_r} /u-boot.bin
reading /u-boot.bin
558296 bytes read in 79 ms (6.7 MiB/s)
# Erasing the SPI NOR flash
=> sf erase 0 3e8000
SF: 4096000 bytes @ 0x0 Erased: OK
# Writing to the SPI NOR flash
=> sf write ${kernel_addr_r} 0 3e8000
device 0 offset 0x0, size 0x3e8000
SF: 4096000 bytes @ 0x0 Written: OK
Resources
- ↑ https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/pull/32553#issuecomment-373915787
- ↑ http://wiki.pine64.org/index.php/PINE_A64-LTS/SOPine_Main_Page#PINE_A64-LTS_Board_Features
- ↑ http://files.pine64.org/doc/Pine%20A64%20Schematic/Pine%20A64%20Pin%20Assignment%20160119.pdf
- ↑ http://linux-sunxi.org/Pine64#FEL_mode
- ↑ https://github.com/ayufan-pine64/bootloader-build/blob/d7e891cbee8a559ea50cf25ee18aa9d7b4ea9d58/blobs/flash-spi.cmd#L11-L13