Mailman
From NixOS Wiki
Running Mailman on NixOS
This example includes:
- Postfix as the MTA
- uwsgi to host Mailman's web interface and archives (Postorius and Hyperkitty)
- nginx to terminate TLS, proxy to uwsgi, and serve static assets
- letsencrypt to acquire TLS certificates for nginx
Deployment steps
- Edit
/etc/nixos/configuration.nixand add this stuff:
{ config, pkgs, ... }:
let
OWNER_EMAIL = "postmaster@example.org"; # Change this!
MAILMAN_HOST = "mailman.example.org"; # Change this!
in
{
services.postfix = {
enable = true;
relayDomains = ["hash:/var/lib/mailman/data/postfix_domains"];
sslCert = config.security.acme.certs.${MAILMAN_HOST}.directory + "/full.pem";
sslKey = config.security.acme.certs.${MAILMAN_HOST}.directory + "/key.pem";
config = {
transport_maps = ["hash:/var/lib/mailman/data/postfix_lmtp"];
local_recipient_maps = ["hash:/var/lib/mailman/data/postfix_lmtp"];
};
};
services.mailman = {
enable = true;
siteOwner = OWNER_EMAIL;
webUser = config.services.uwsgi.user;
hyperkitty.enable = true;
# Have mailman talk directly to hyperkitty, bypassing nginx:
hyperkitty.baseUrl = "http://localhost:33141/hyperkitty/";
webHosts = [MAILMAN_HOST];
};
# Make sure that uwsgi gets restarted if any django settings change.
# I'm not sure why this isn't covered by the "before" and
# "requiredBy" settings present in mailman-web.service. Maybe
# because it's a oneshot and not a daemon?
systemd.services.uwsgi.restartTriggers = [
config.environment.etc."mailman3/settings.py".source
];
# Tweak permissions so nginx can read and serve the static assets
# (otherwise /var/lib/mailman-web is mode 0600)
systemd.services.mailman-settings.script = ''
chmod o+x /var/lib/mailman-web
'';
services.uwsgi = {
enable = true;
plugins = ["python3"];
instance = {
type = "normal";
pythonPackages = (
# TODO: I hope there is a nicer way of doing this:
self: with self.override {
overrides = self: super: { django = self.django_1_11; };
}; [ mailman-web ]
);
# uwsgi protocol socket for nginx
socket = "127.0.0.1:33140";
# http socket for mailman core to reach the hyperkitty API directly
http-socket = "127.0.0.1:33141";
wsgi-file = "${config.services.mailman.webRoot}/mailman_web/wsgi.py";
chdir = "/var/lib/mailman-web";
master = true;
processes = 4;
vacuum = true;
};
};
security.acme.email = OWNER_EMAIL;
security.acme.acceptTerms = true;
services.nginx = {
enable = true;
recommendedGzipSettings = true;
recommendedProxySettings = true;
recommendedTlsSettings = true;
virtualHosts.${MAILMAN_HOST} = {
enableACME = true;
forceSSL = true;
locations."/static/".alias = "/var/lib/mailman-web/static/";
# If you're coming from Mailman 2, you might want these redirects:
# locations."~ ^/(?:pipermail|private)/([a-z-]+)/".return = "303 https://${MAILMAN_HOST}/hyperkitty/list/$1.${MAILMAN_HOST}/";
# locations."~ ^/(?:listadmin)/([a-z-]+)".return = "303 https://${MAILMAN_HOST}/postorius/lists/$1.${MAILMAN_HOST}/settings/";
# locations."~ ^/(?:listinfo|options)/([a-z-]+)".return = "303 https://${MAILMAN_HOST}/postorius/lists/$1.${MAILMAN_HOST}/";
# locations."/create".return = "301 https://${MAILMAN_HOST}/postorius/lists/new";
locations."/".extraConfig = ''
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:33140;
include ${config.services.nginx.package}/conf/uwsgi_params;
'';
};
};
networking.firewall.allowedTCPPorts = [ 25 80 443 ];
}
- Install and start the services:
[root@mailman:~]# nixos-rebuild switch
- Generate initial
postfix_domains.dbandpostfix_lmtp.dbdatabases for Postfix:
[root@mailman:~]# sudo -u mailman mailman aliases
- Create a django superuser account. Be careful to run this only as the
uwsgiuser in/var/lib/mailman-webor you will run into permission problems later.
[root@mailman:~]# cd /var/lib/mailman-web [root@mailman:/var/lib/mailman-web]# sudo -u uwsgi mailman-web createsuperuser ### Using settings module from /etc/mailman3/settings.py #### Username (leave blank to use 'uwsgi'): root Email address: postmaster@example.com Password: Password (again): Superuser created successfully.
- Navigate to
https://<your_mailman_hostname>/adminin a web browser and login to the Django admin interface:
- Navigate to
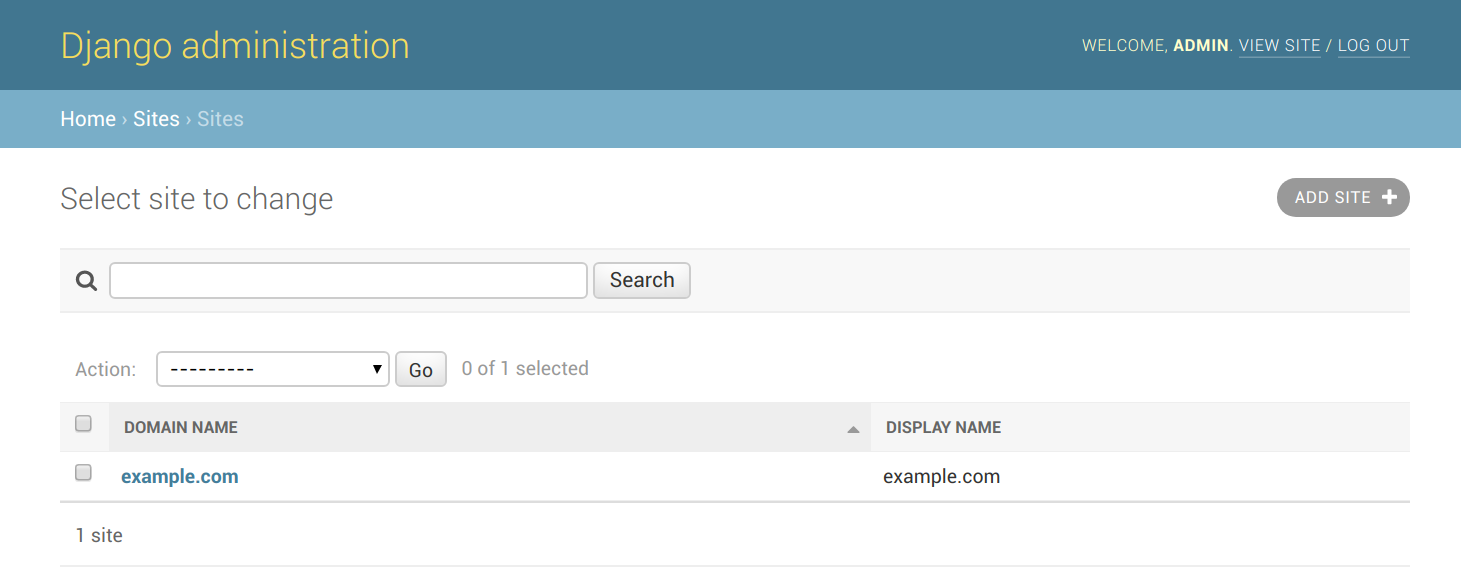
https://<your_mailman_hostname>/admin/sites/site. Click on the example.com site, change it to your desired domain name, and hit Save. This configures the web serving domain, not the domain used for email.
- Navigate to
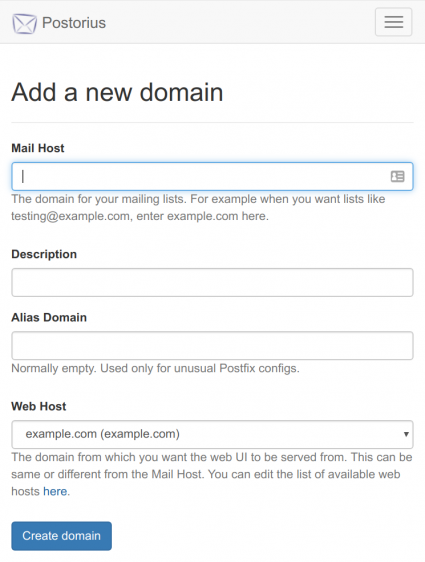
https://<your_mailman_hostname>/postorius/domains/new/. Fill in the form to add the domain you wish to use for mailing list email addresses.
At this point you should have a working Mailman installation. Create and manage lists using the web interface or the mailman commandline tool, and refer to the upstream documentation for lots more information.
Optional extras
Social logins
Mailman 3 uses django-allauth to allow logins via many external auth providers, such as GitHub and Google. To enable these we need to update our Django settings and add some per-provider specifics in the admin UI.
In this example we're just adding GitHub, but there are lots of other providers available.
- Add to your
configuration.nixand runnixos-rebuild switch:
# Extend the django settings.py directly since this can't all be
# done via JSON settings (services.mailman.webSettings)
environment.etc."mailman3/settings.py".text = ''
INSTALLED_APPS.extend([
"allauth.socialaccount.providers.github",
])
'';
- Register a new OAuth application on GitHub at https://github.com/settings/applications/new. Your Authorization Callback URL will be
https://<your_mailman_hostname>/accounts/github/login/callback/. Save the Client ID and Client Secret that GitHub gives you at the end of this process.
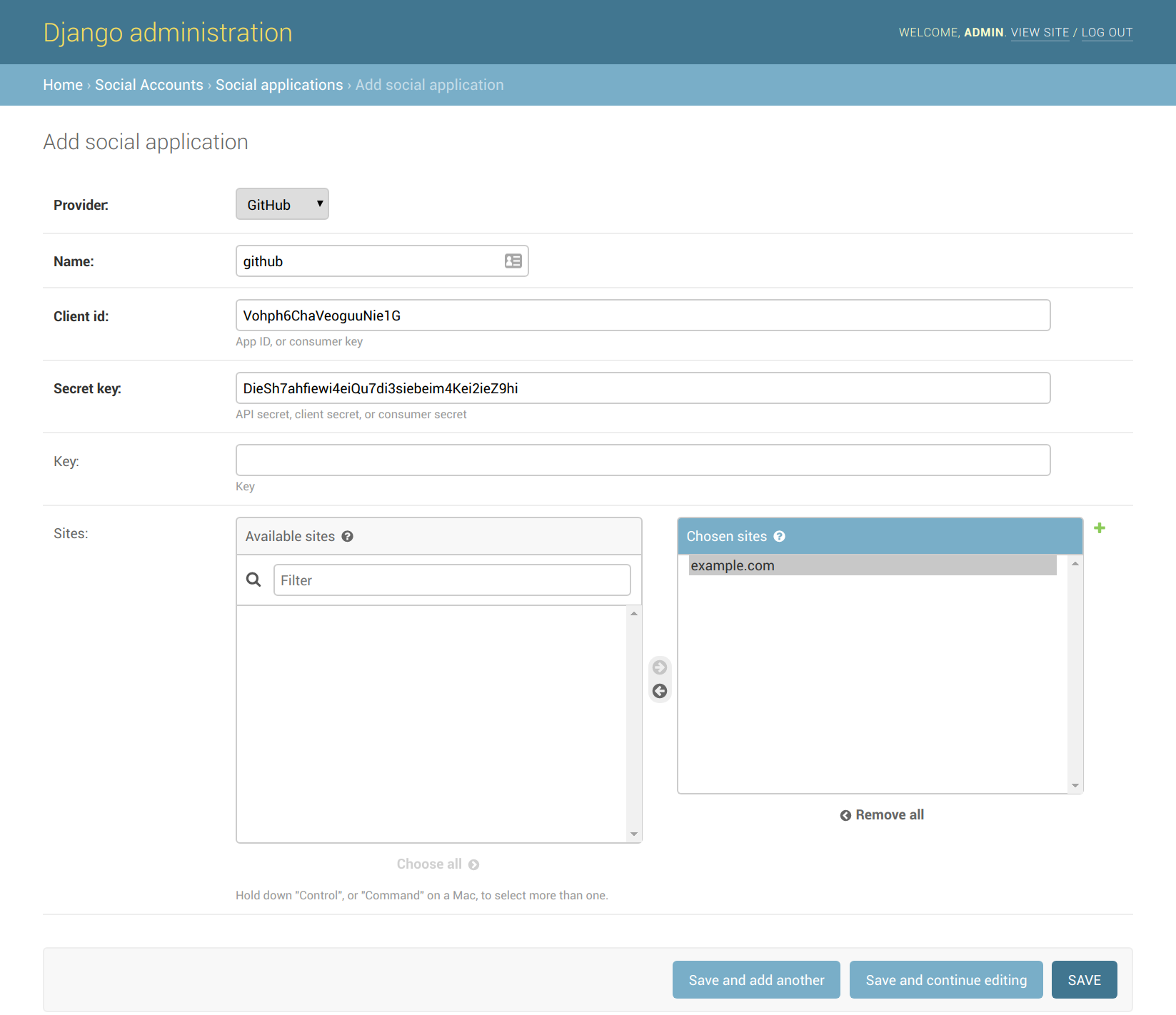
- Navigate to
https://<your_mailman_hostname>/admin/socialaccount/socialapp/add/and fill in the values you got from GitHub. Make sure you click Choose all to enable this auth provide for your django site, then click Save.
Now you should be able to login to your mailman site with GitHub, and see your account's connections at https://<your_mailman_hostname>/accounts/social/connections/